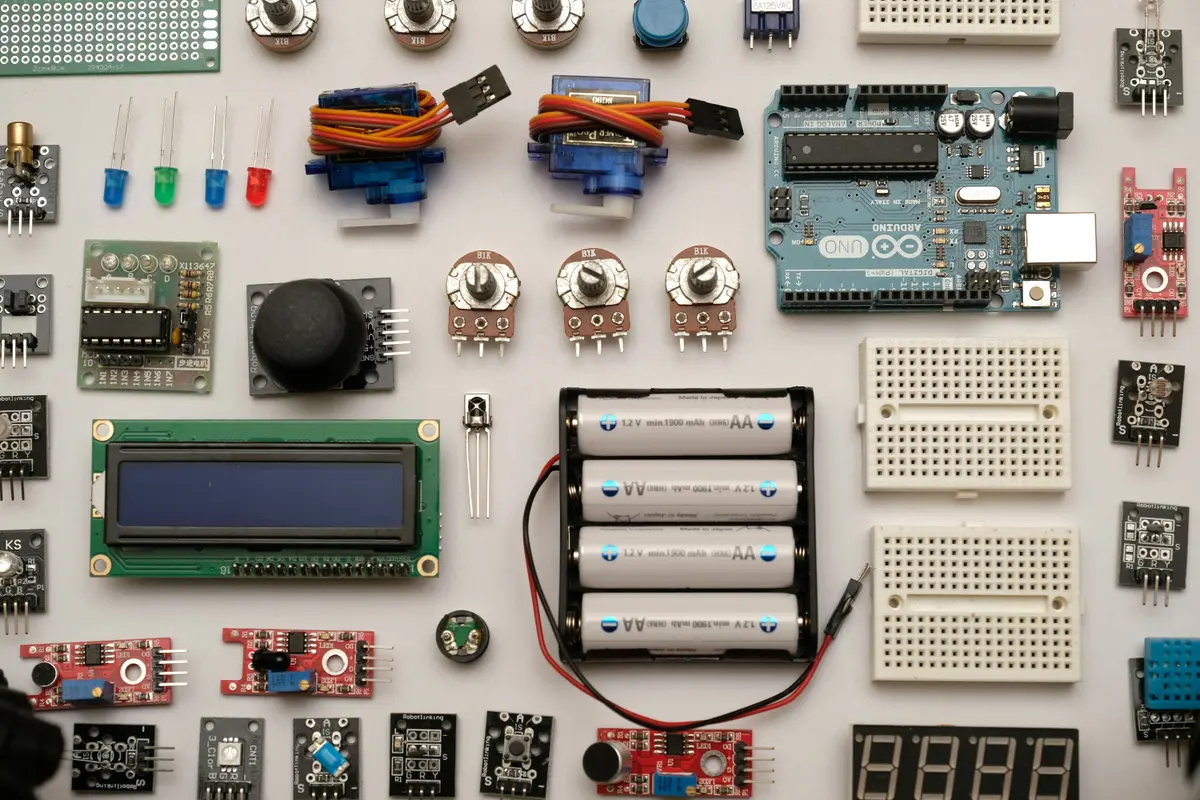
The Internet of Things (IoT) is changing our interactions with technology by effortlessly linking physical devices to the Internet, facilitating real-time communication and automation. In this blog, we will explore IoT devices, discussing their architecture, components, applications, and the vital role they play in contemporary technology.
What Are IoT Devices?
IoT devices are physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data with other systems via the Internet. These devices vary from household items to advanced industrial equipment.
Common IoT Devices
| Device Type | Description | Examples |
|---|
| Wearables | Devices that gather personal data from the body. | Smartwatches, fitness trackers |
| Smart Home Devices | Appliances that automate home functions. | Smart thermostats, smart locks |
| Industrial IoT Devices | Tools for manufacturing and logistics. | Sensor-equipped machines, robots |
| Healthcare IoT Devices | Devices monitoring patient health. | Remote patient monitors, pill dispensers |
IoT Device Architecture
IoT systems typically consist of four main layers:
- Perception Layer: Devices like sensors and actuators gather information from their surroundings.
- Network Layer: Transmits data to other systems or the cloud.
- Processing Layer: Analyzes data and applies intelligence.
- Application Layer: Provides the user interface for monitoring and management.
Mathematical Model of IoT Data Flow
The data flow in IoT systems can be modeled as:
Dsensor=Rdata×t
Where:
- (Dsensor) is the total data in bytes,
- (Rdata) is the data rate in bytes per second (bps),
- (t) is the time in seconds.
This equation shows how data accumulation grows based on the sensor data rate.
Key Components of IoT Devices
| Component | Function | Example |
|---|
| Sensors | Collect data from the environment (e.g., temperature). | Temperature sensor in a smart thermostat |
| Actuators | Execute actions based on processed data. | Motor in smart locks |
| Microcontroller | Handles data and exchanges information with other devices. | ESP8266 in smart lights |
| Connectivity | Enables communication via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc. | Zigbee or Wi-Fi module |
Real-World Example: IoT in Smart Homes
Let us consider a smart thermostat:
- Sensors detect the room temperature.
- Microcontroller processes the temperature data and checks against the preset temperature.
- If the temperature is too low, the actuator triggers the heating system.
- Data is sent via Wi-Fi to a cloud service, allowing the homeowner to monitor the system remotely.
For an IoT system to be efficient, energy consumption (Etotal) should be minimized. It can be represented as:
Etotal=i=1∑nPi×ti
Where:
- (Pi) is the power consumed by each device component (i),
- (ti) is the operational time of component (i),
- (n) is the number of components.
This formula helps design energy-efficient IoT devices, which is particularly important in battery-powered systems.
Popular IoT Applications
| Application | Sector | Example |
|---|
| Smart Homes | Consumer | Smart lights, voice assistants (Amazon Echo) |
| Healthcare | Medical | Remote monitoring, health trackers (Fitbit) |
| Automation in Industry | Production | Predictive maintenance, robotics |
| Smart Cities | Urban Development | Smart streetlights, traffic management systems |
Security Concerns in IoT Devices
With good connectivity comes great responsibility. IoT devices often face security risks such as data breaches, malware attacks, and unauthorized access. To secure IoT systems, it's crucial to:
- Encrypt data transmitted between devices.
- Update firmware regularly to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use strong authentication methods like two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Monitor device activity for unusual patterns.
Conclusion
IoT devices have transformed industries by enabling automation, data collection, and enhanced control. As the IoT ecosystem grows, understanding the core components, architecture, and applications of IoT devices will help you harness the full potential of this technology in your personal or professional projects.
Credits
- Photo by Robin Glauser on Unsplash